Automatic sleep tracking
Tracks sleep automatically, without the need to manually start it.
On smartphones, sleep tracking was traditionally a process initiated by a button tap, or by a hard timed trigger.
Sleep as Android is different.
The app offers smart ways to track your sleep automatically similarly to what wearables and smart bands do — using your phone’s activity recognition system.
Sleep app also have a feature for tracking sleep times - Sleep time estimation. If you forget to start sleep tracking, the app estimates the most probable times you were sleeping form phone activity recognition engine and Google Sleep API, and will ask you next day. You can read more about sleep time estimation here.
Settings → Sleep tracking → Automatic sleep tracking → Start sleep tracking → After fall asleep
|
|
If you do not see this option your phone probably does not support activity tracking in background. This is based on the phone hardware, more specifically the SoC’s sensor batching queue size. |
1. Manual only
Sleep as Android will never start sleep tracking without you pressing the Start sleep tracking button with the moon icon, from the wearable, or with a tracking widget.
2. Bedtime
This is a very simple automatic option which starts sleep tracking at the start of your bedtime. See how is the bedtime determined here. This is useful only if you have a very regular sleep schedule.
3. Smart period
Again a simple automation which starts sleep tracking some time before the smart period. The aim of this option is to have a function Smart wake-up with minimal battery use. Using this option will provide you with incomplete sleep stats.
|
|
Sleep tracking starts 45 minutes before the smart period, so the sensor has enough time to gather data for calibration. |
4. After fall asleep
This is the most advanced automatic option where all the sophistication goes in. It uses input from your phone’s activity recognition engine and uses your common sleep habits for different days of week to find the sleep times for you.
Automatic start after fall asleep is a breakthrough method invented by Urbandroid which uses Google Activity Transition API or Google Sleep API as a base to detect when you’ve gone to bed to start sleep tracking.
First, we need to find intervals when it is most probable that you’d be sleeping. By default, the interval we use is 8PM to 7AM, but this will shift over time to reflect your habits.
Because the algorithm learns from your typical patterns it is a good idea to help it from time to time and if you have the chance press the moon button just to give it an extra hint to improve accuracy.
There are several factors that play into how the intervals are found out:
-
Your activity
Google’s Activity Transition API -
Your sleep history
We’re looking for regularities – for example “when do you usually go to sleep on Tuesdays”. -
Your alarm
Setting an alarm gives the app a very important hint on when you might be sleeping. We subtract your ideal sleep time from your alarm time and check whether this time is +-4 hours from the interval suggested by the other factors.
We expect your sleep to be somewhere in this interval +/- an hour or two.
So when we have found out the most probable sleep interval, we can zoom in and look at your activity with a little more precision to find when exactly do you go to sleep.
Every 15 minutes during the previously detected “probable sleep interval”, we check the state of your phone in the Google Transition API, and if we detect a still state, we start a sleep tracking service, using whatever sensors you have configured (accelerometer, sonar, wearables, …).
Also every 15 minutes we do corrections based on your activity and either stop the current sleep tracking without saving or add awake intervals if we already track for long enough (at least 45 minutes).
Automatic tracking attempts are stopped quickly (~half a minute) after we recognized you are probably still awake if one of the following holds:
-
Awake-like activity on the phone sensor
-
Your phone has screen on, is in upright orientation probably hold in hands as there is a subtle shake
-
Awake-like activity on the watch sensor if smart watch is connected and in reach
-
Noise recording (and snoring detection) is enabled and talking is detected
|
|
When using Sonar automatic sleep tracking (after fall asleep) only starts when the phone is charging. The reason for this is battery consumption which is usually high with sonar. |
FAQ
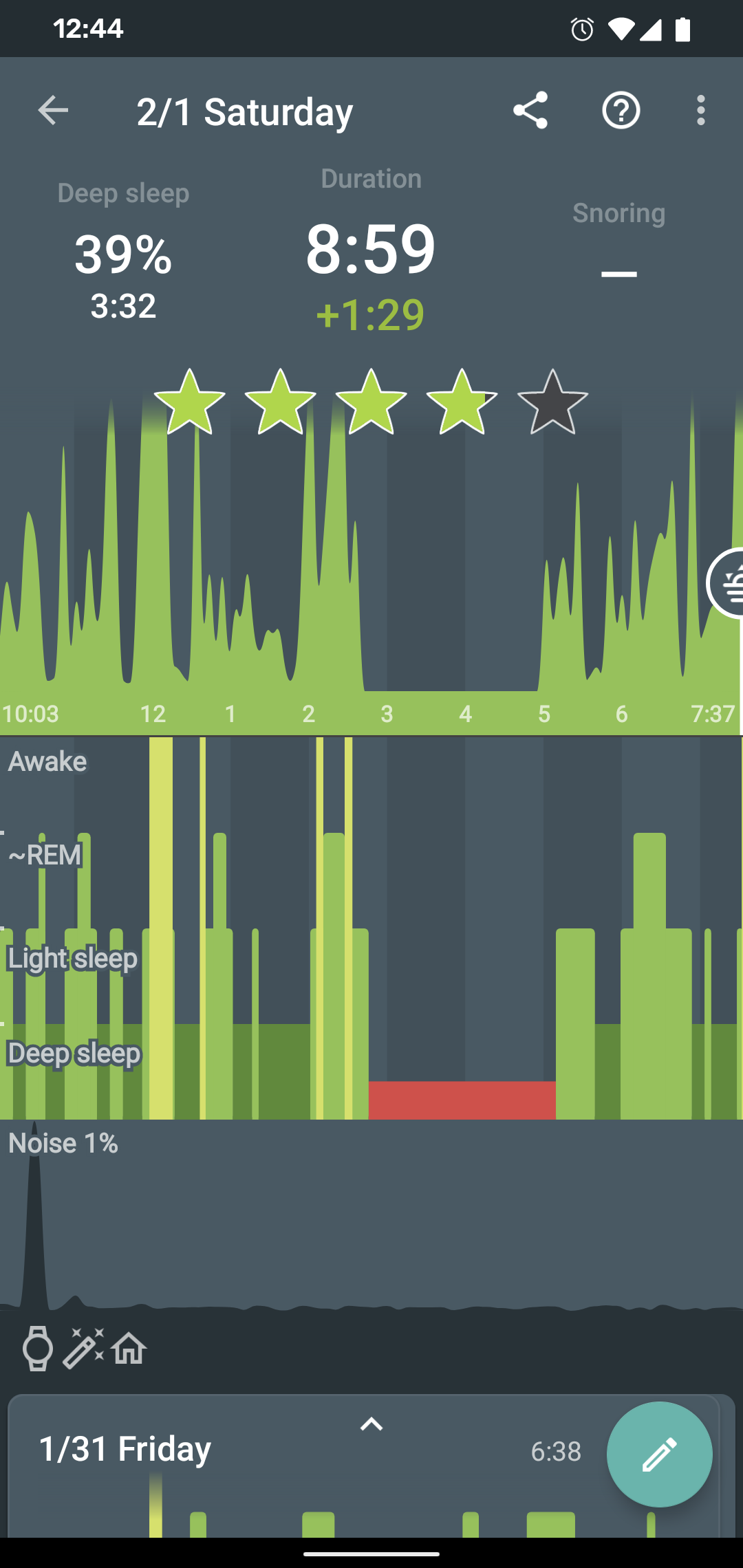
Sleep duration is the sum of all your sleep stages (light, REM, and deep), not including waking stages - because you are not really sleeping when you are awake.
So on default settings, your Sleep Duration ,ay be a little shorter than your tracking time.
If you want your sleep duration to be the same as your tracking duration:
-
Disable the awake detection in Settings → Sleep tracking → Awake detection.
-
You can also try to adjust the sensitivity of each type of settings to get optimal results. In most cases, too many awake periods are caused by significant HR peaks.
-
If you are not sure, where these awake periods are coming from, please use the Left ☰ menu →
Support →
Report a bug, and send us the application log.
Smart Bluetooth allows us to collect HR data from a non-compatible wearables, or oximeters.
-
Enable the tracking in Settings → Sleep tracking → Wearables →Bluetooth Smart (may be hidden in the Advanced section).
-
Try pairing with your device (this may not be necessary for all devices and OS versions).
-
Make sure that no other app is using your device during sleep tracking.
If nothing helps please send us a debug report using Left ☰ menu → Support →
Report a bug..
|
|
BT Smart heart rate tracking only works from Android 4.3 onward |
We use a different input than polysomnographists, and define our own sleep phases, reflecting an objective aspect of sleep, easy to measure with common devices. One naturally needs to ask whether there is any relationship between the EEG-phases and our ACT-phases.
Fortunately, several research teams raised similar questions before (See this one, or this one, or this one, or this one). They measured a bunch of people on a traditional polysomnograph and recorded their physical activity at the same time (By filming them and then counting the movements manually, or by using accelerometer readings). The published analyses show that there indeed is a significant statistical relationship between EEG-phases and body movements.
You can also read about comparison of Sleep as Android algorithms and Sleep lab results on our blog here.
Battery saving mode currently resumes full tracking before the Smart Wakeup period to find the best time for you to wake up so that tracking uses only a fraction of the battery consumption for the entire night. When the battery drops below your defined standby threshold (default: 10%), the battery saver mode will resume.
Accelerometers are really sensitive, which is great for sleep tracking. Usually what you see when you leave the phone on the table is immediately dwarfed when you make a more significant movement. Just leave the phone on the table for a while and you will see a dramatic spike, but then move the phone and you will see that all the development is really tiny compared to the new peak.
So what you see is random noise caused by very small vibrations of the table or in very quiet areas by seismic movement. We mark the data relatively, so you can always distinguish between light and deep sleep. However, the algorithm works well only in conditions, it assumes i.e. in the bed with relatively large movement peaks.
To be more precise, if you leave the phone on a table, you may get values perhaps in the range of 0.000001 to 0.000009 m/s2 (the value is made up here, but it is physically very small). In the bed, you can get values from 1 to 9 m/s2 (which is physically large). However, the algorithm only sees that the high value is 9 times higher than the low value in both cases.
We had to do this because each accelerometer (in different phones) measures differently, so we couldn’t assume a standard conversion formula that responds to absolute values.
So if you use the phone in bed, it is indeed drastically different from measuring in a quiet place, like the table.
Please do not hesitate to contact support@urbandroid.org for clarification. You can also read more about how our data compares to sleep lab results at in this post.
This depends on several factors. The general rule is to not allow the pet to move your phone, ideally only your movements should move the device. So in this case it’s best to place Your device either under the pillow or to have an armband or smartwatch/smartband. If your pet is a calm one, it may just work. However, if your pet is used to jump in and out of bed several times a night, the sleep tracking will most probably register these events as light sleep occurrences.
Ultrasound is generally considered safe if it is at normal volume. Regarding health effects, it works in a similar way to normal audible sound, i.e. very loud ultrasound can damage your hearing, whereas at low volume it is safe to hear. When using speakers, smartphones are nowhere close to be able to produce such loud sounds as to damage your hearing.
We also use ultrasound that is very close to the hearing range (around 20 kHz), so the effects of the ultrasound are almost identical to hearing a high pitched sound at the same volume (expect you can’t hear it at all).
The ultrasound volume we use is around 40 dB – which is lower than normal speech volume. You can measure the sound level yourself using e.g. this app.
For pets that are able to hear it, the ultrasound emitted from Sleep as Android is a constant low noise. The situation is similar to e.g. refrigerator noise. It is there, you can hear it, but it’s not so much disturbing. The ultrasound definitely cannot damage your pets hearing at the volume used in Sleep as Android.
Bats can be confused and fly into walls.
The only difference between normal audible sound and our sonar is that the frequency is a little higher (normal frequencies 2 Hz-20 kHz, our sonar frequencies 18 kHz-22 kHz). This is so small difference for the mic and speaker membranes that there is definitely no chance of damage, even with prolonged usage.
Usually this is not caused by the sleep tracking directly as this is usually not consuming too much resources (usually around 1-3% battery per hour of tracking).
The issue appears because we hold a wake lock (keeping the phone awake) – any badly written apps may access the CPU extensively during the sleep tracking time. We suggest checking which services are running before you get to sleep.
For us it is hard to debug this. Also battery statistics are not a hint here as all battery consumption is accounted to the app which holds the lock even it did not consume the battery – this is by design in Android.
To conclude, this issue may happen, although we did not get any similar reports for a very long time now. But the most probable cause is some wrong 3rd party service or app on your device.
To see more on the issue we would need a debug report (menu > report a bug).
A good test would be to reboot your phone before sleep tracking (or kill any unnecessary services running) and see if that helps.
At first Sleep as Android may look complex with all its options, but in fact it is fairly easy to get started improving your sleep and wake up.
You can delve deep into all the amazing options Sleep as Android provides later on. But to get started just rely on our carefully selected defaults.
-
Use the top right plus icon to set up your Alarm time (e.g. 8:00). Tap the desired time directly on the clock - hours first, minutes second.
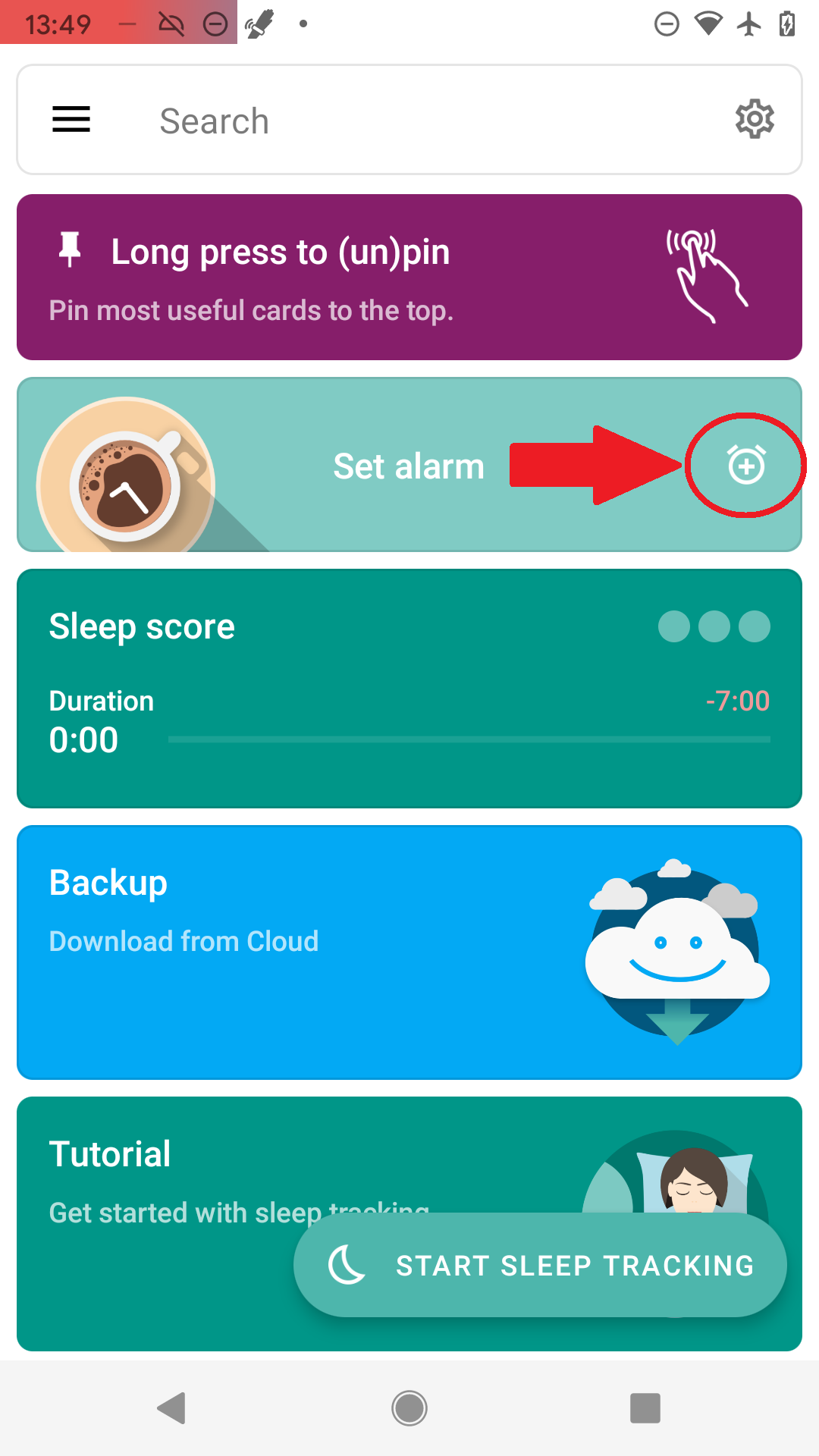 Figure 1. Tap on the (+) icon
Figure 1. Tap on the (+) icon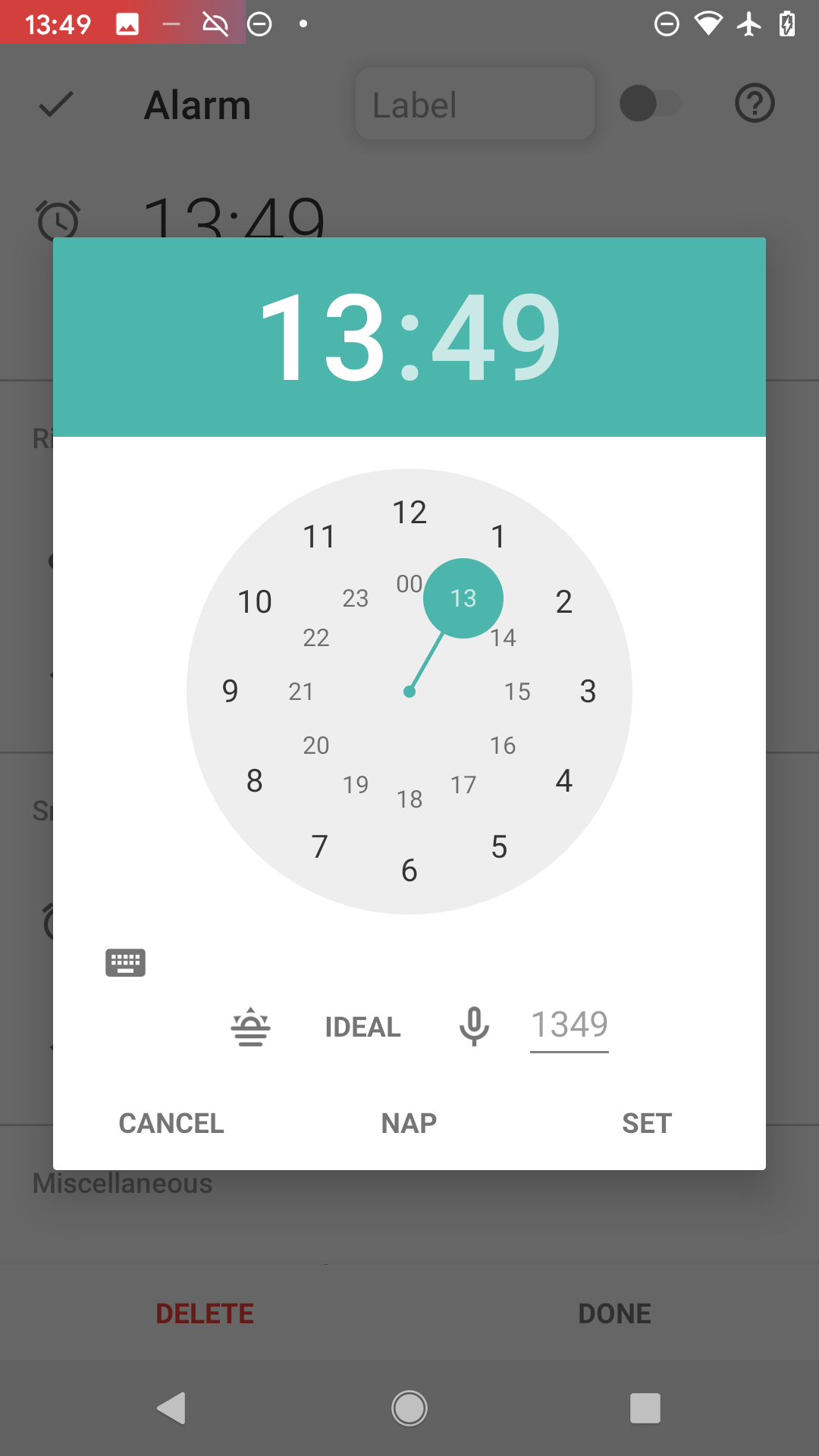 Figure 2. Tap on the desired time - hours first
Figure 2. Tap on the desired time - hours first Figure 3. Tap on the desired time - minutes second
Figure 3. Tap on the desired time - minutes second -
Confirm the selected time with SET button, it will show you the new alarm settings. Confirm the alarm with DONE.
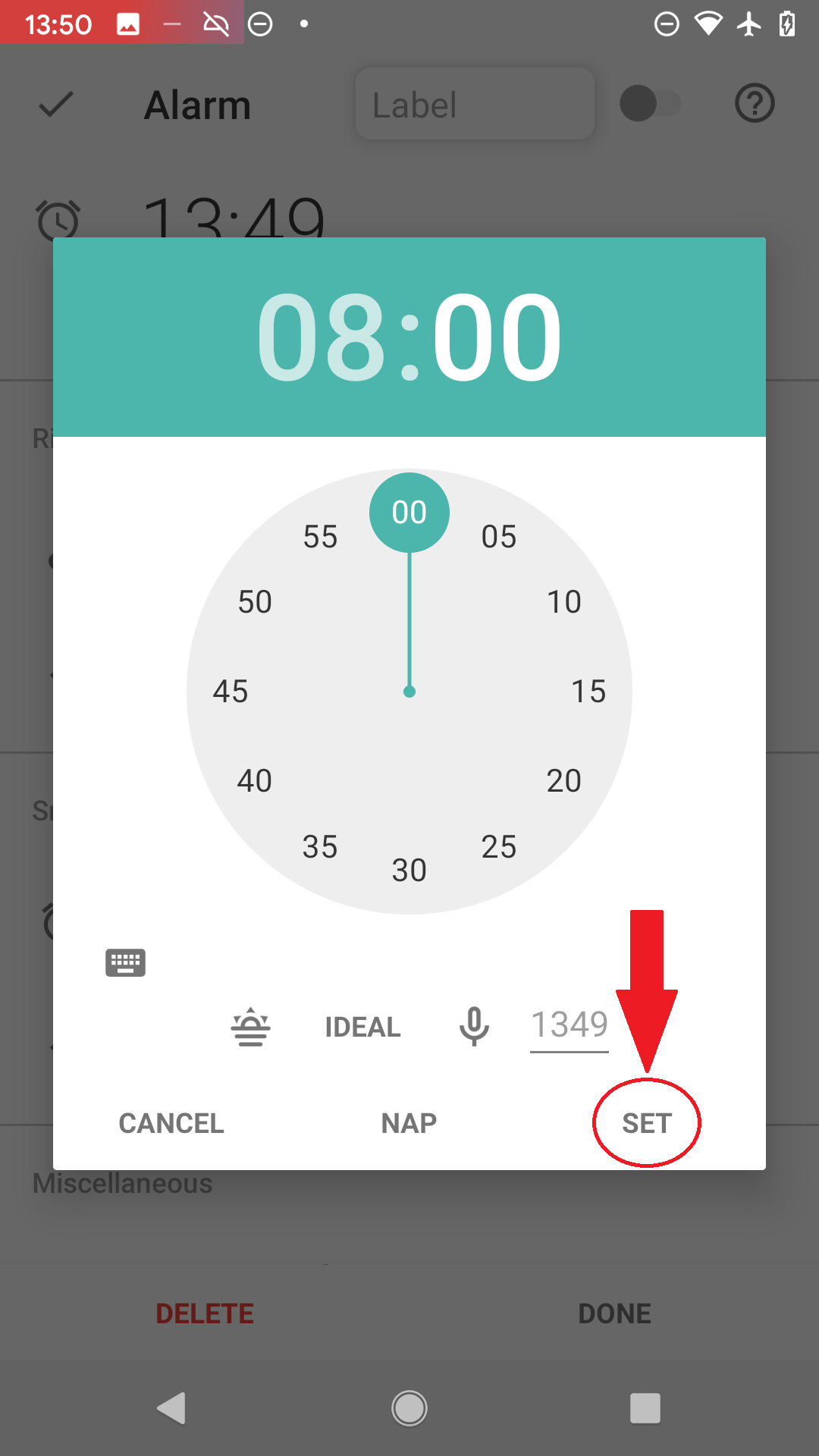 Figure 4. Confirm the time with SET button.
Figure 4. Confirm the time with SET button.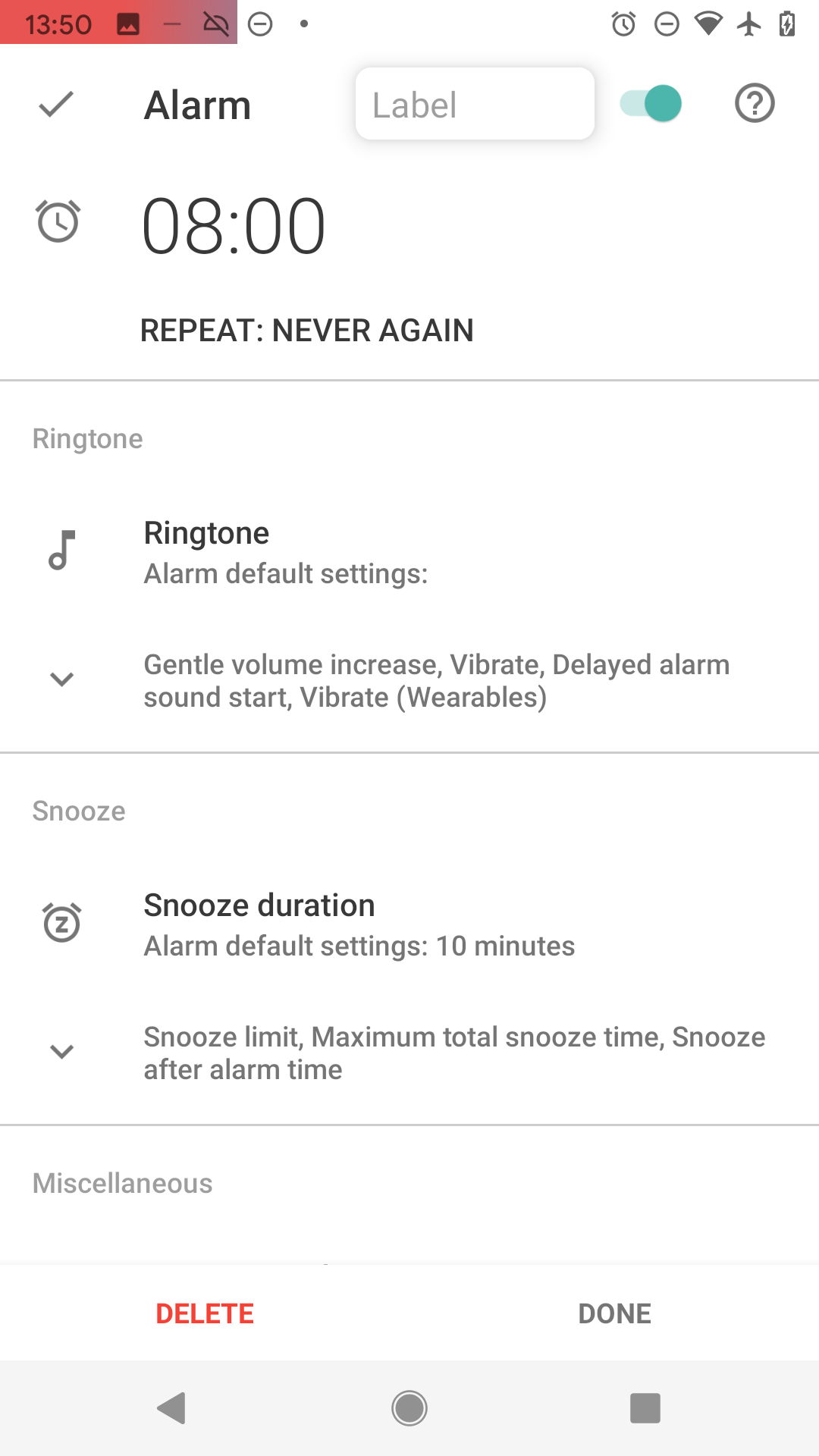 Figure 5. Now you see the new alarm’s settings.
Figure 5. Now you see the new alarm’s settings.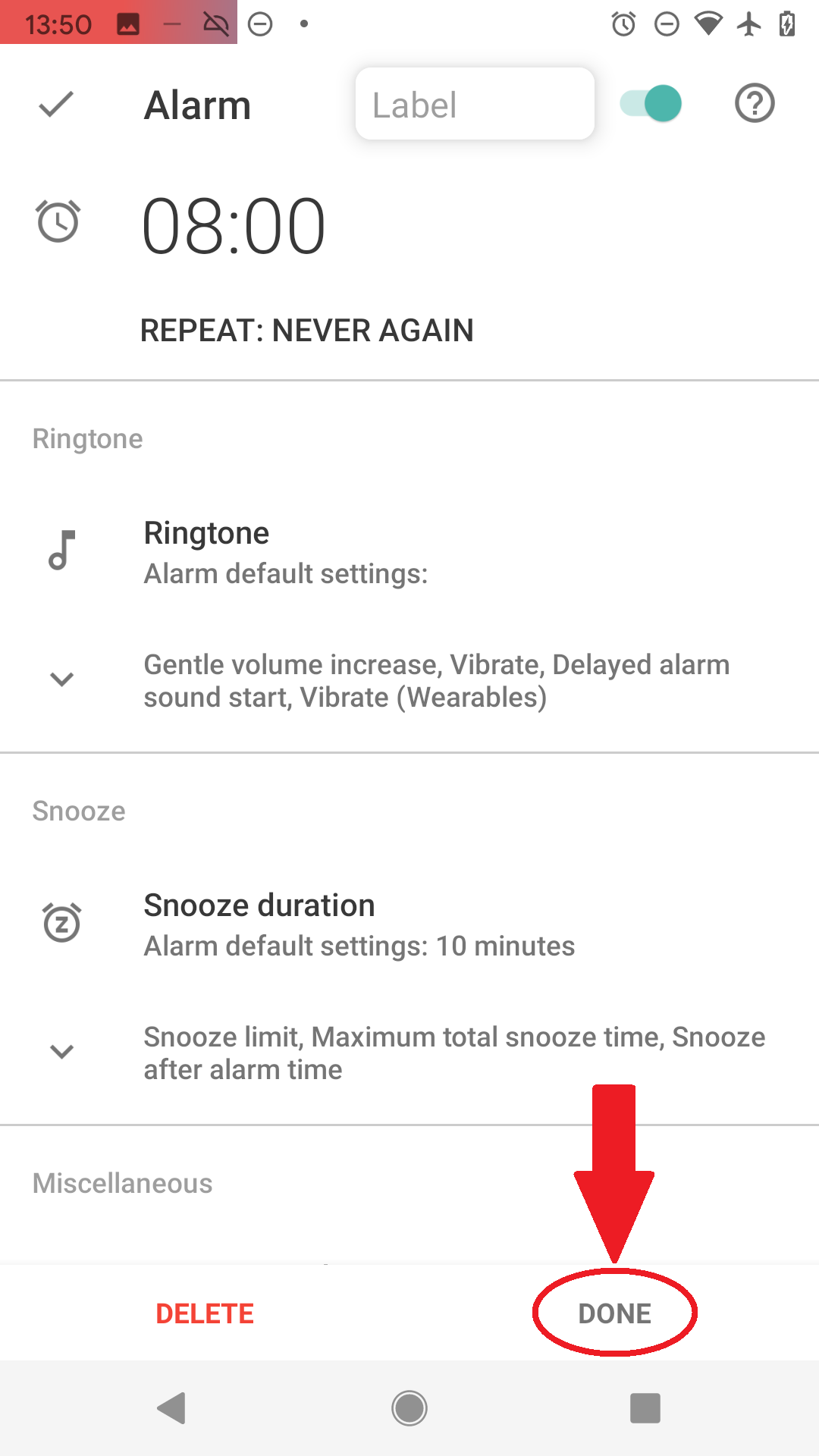 Figure 6. Confirm with DONE
Figure 6. Confirm with DONE -
Smart wake up makes sure to find the best time for your wake up between 7:30 – 8:00 based on your sleep cycle.
-
You can now see the alarm scheduled on the main screen.
-
Tap the moon and Sleep tracking starts, we use your phone’s sensor to find out what sleep phase you are in (see How it works).
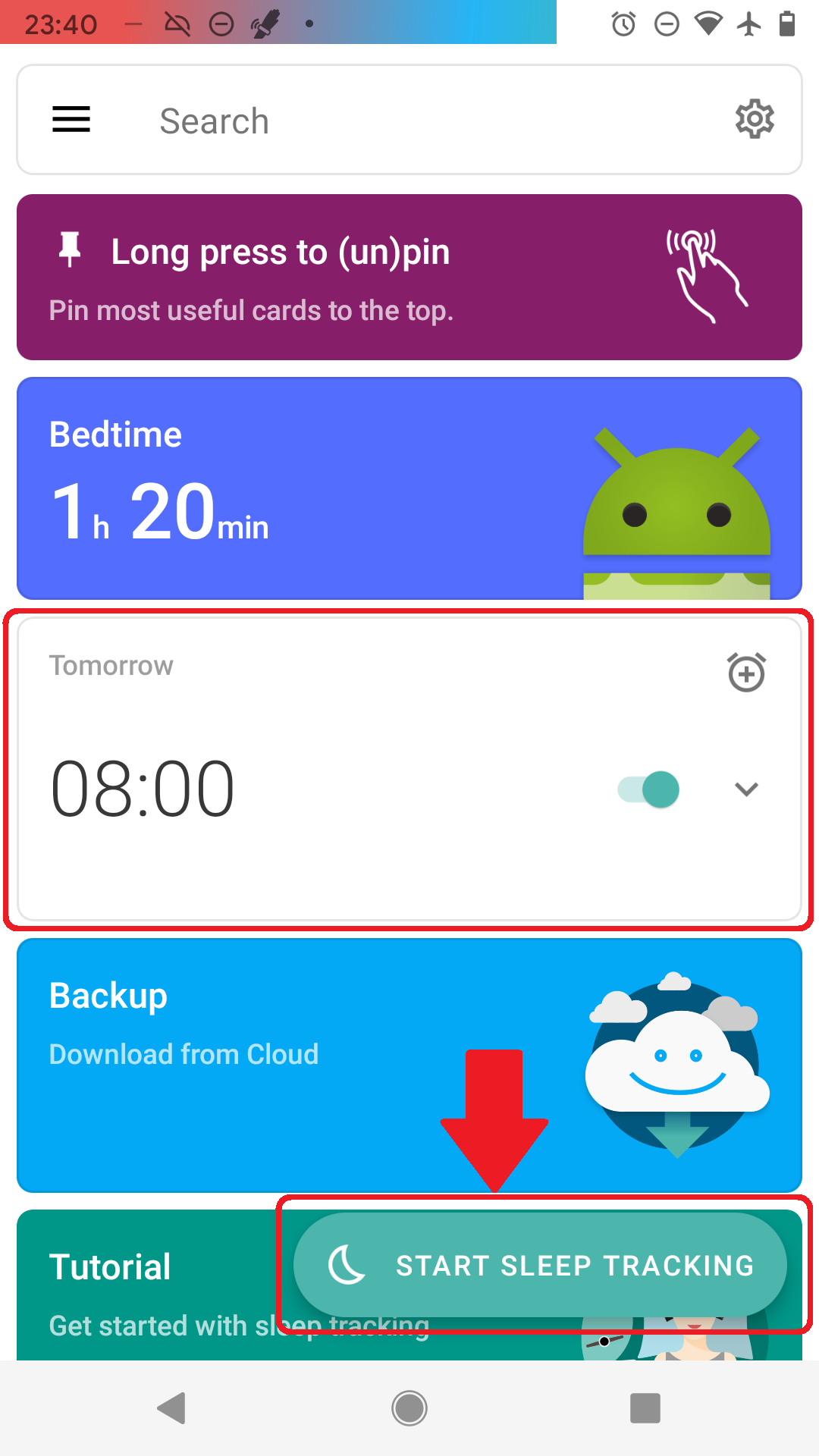
We recommend turning on airplane mode during sleep tracking -
Now just place the phone on the mattress near your body (see Setup sleep tracking) so it is able to sense your movement and wake you in the right sleep phase to bring your wake up experience to a new level
-
After dismissing the alarm in the morning you will see your sleep phases, deep sleep % and more..
This can be the result of several things, so please try the following troubleshooting steps:
-
Make sure you have Sleep as Android Gear Addon installed on your phone and updated to the latest version.
-
It may happen that the addon can not be started by us if it was force stopped before. In this case, please go to the Play Store app on your phone, open addon page, tap "OPEN".
-
Disable all battery savers on your phone for all involved apps (Sleep as Android, Sleep as Android Gear Addon, Samsung Accessory Services) - to find out how to do this, please visit dontkillmyapp.com
-
Samsung Accessory Services sometimes misbehaves and prevents 3rd party apps from connecting to the watch. Please uninstall and reinstall it.
We have had reports of audible artifacts during sonar tracking on some devices. It sounds like this:
Some of the signal gets into the audible range, probably due to either insufficient speaker quality or some post-processing applied to the output by your device’s firmware.
We also have some reports that Sonar can suddenly become audible while tracking at night. Unfortunately, we are not sure why this might happen, we have very few such reports, and we are not able to reproduce this on our phones.
To make any audible artifacts less likely:
-
Go to Settings → Sleep tracking → Test Sensor.
-
Try a different frequency from the drop-down menu list.
-
When you find the least affected frequency, you can try lowering the volume a bit (the slider). But keep it as high as possible to get reliable results.
|
|
If the volume needs to be adjusted, always confirm that sonar is still working - ideally after you change settings, try to sit calm in font of the test for few seconds and than move slightly - do you see a spike? |
If you get completely flat graphs with automatic tracking with sonar sensor after upgrading to Android 11, make sure the app has permission Draw over other apps, Display over other apps or Appear on top (Samsung).
This permission is necessary for accessing the microphone from the background.
-
System settings → Apps → Sleep → Appear on top / Display over other apps
-
System settings → Apps → More options (⁝) > Special access > Appear
on top / Display over other apps
If the tracking stops completely after few minutes, the background processes are restricted by your system.
-
Make sure no system restrictions are applied to Sleep as Android, or any companion app for a tracking with wearable: Check our guide here.
-
If the guide won’t help, send us your log using Left ☰ menu →
Support →
Report a bug.
-
Please make sure that you are not accidentally starting the Sleep as Android app from your watch. This would start sleep tracking immediately.
-
Make sure you are not using automatic start of sleep tracking in Settings → Sleep tracking → Automatic sleep tracking → Start sleep tracking.
You can find more information about automatic sleep tracking start here.
If you notice your volume gradually dropping after a while while tracking is running, the Turn off when sleeping is enabled. This feature lowers the system-wide volume, so it also affects music played outside of Sleep.
-
Go to Settings → Sleep tracking → Lullabies → Turn off when sleeping.
-
Increase the minimum play time (5-90 minutes).
-
Or disable the feature altogether by setting it to Disabled, and the app won’t change the volume.
|
|
When tracking with sonar, the volume must be kept at maximum to maintain reliable results. |
Unfortunately, this also affects media volume in third-party applications, and we cannot control those separately from Sonar’s media volume. This means that while using Sonar, you can only use media applications at full volume.
You can set a time delay to start tracking in Settings → Sleep Tracking → Awake Detection → Delayed Sleep Tracking.
- External Players
When using Sonar, you cannot use the volume buttons to control the media volume because it always jumps back to maximum.
- Lullabies
You can control the volume of lullabies from the Sleep app (Settings → Lullabies) and from Lullaby add-on pack - when you lower the volume with the volume buttons, the lullaby volume is estimated and adjusted accordingly, the Sonar volume is still kept at maximum.
Usually the battery consumption issue or related issues that cause the phone to overheat during sleep tracking are not directly caused by sleep tracking.
In most cases, sleep tracking itself does not consume too much battery (usually around 1-2% per hour of tracking). But because we keep a wake lock (keeping the phone awake), any other apps and processes can access the CPU extensively during the sleep tracking time. We would suggest checking what services are running before you go to sleep. Also, battery statistics are not a clue here, as all battery consumption goes to the app holding the wake lock, even if it did not consume the battery (this is by design in Android). This is hard for us to debug.
A good test would be to restart your phone (or kill any unnecessary services running) before using Sleep as Android and see if Sleep as Android still uses too much battery after that. One of the features of Sleep as Android that may cause higher CPU load during tracking is the noise recording. You can try tracking without it as a reference. We also strongly recommend tracking with airplane mode enabled.
The red block indicates that something went wrong with tracking at that time and the device stopped providing sensor data for some reason. Usually those are some non-standard battery optimizations or battery savers, the battery gets too low so we preserve it for the alarm or connectivity issue if you use a wearable.
1. Battery restrictions
Make sure no system restrictions are applied to Sleep, or any involved apps like wearable companion app).
See our guide here, and follow the instructions.
2. Too low battery
When the battery is too low (usually below 10%), data collecting is terminated to preserve enough battery for alarm.
When the battery was too low, there is a battery icon is displayed on the graph:
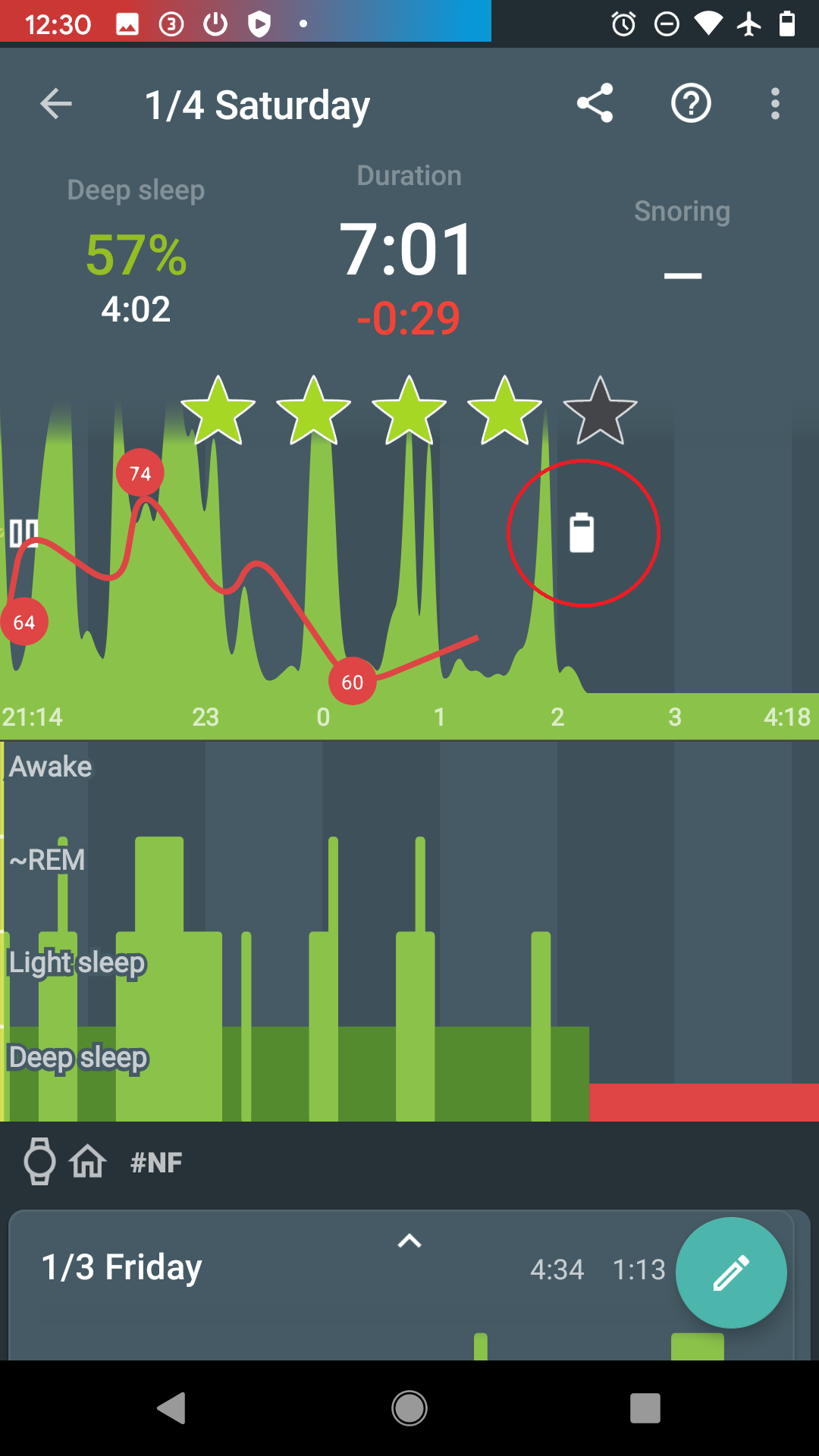
3. Connectivity issues with a wearable
When the connection with the wearable is lost, you can see red sections on the graph. The app always tries to reach the wearable again.
The graph can look like this:
-
Opt-out from any battery restrictions is applied by your system (https://dontkillmyapp.com/)
-
Pair the wearable with your phone in System settings.
-
Make sure the BT is not lost, and try lowering the distance between the phone and the wearable.
-
Try settings the device as Trusted device.
Unfortunately, due to security restrictions introduced by the Android team in 4.2, there is no way to automatically enable airplane mode from an app. You always have to go into settings or long press the power button. If you have a rooted phone you might consider using https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=lv.id.dm.airplanemh we have support for this in Sleep. A similar hack exists for 4.3.
If you don’t agree with the Android team’s design decision, you can upvote issue 40497 here http://code.google.com/p/android/issues/detail?id=40497.
There is no clearcut answer to which day the sleep between them belongs.
We have decided to attach the sleep to the day after, because how you slept will largely determine how your day will be.
If you have separate mattresses there is minimum interference from your partner. If you have one big shared mattress (which isn’t recommended as you partner may need different mattress for his healthy sleep), it could still work assuming you keep your phone close to your body and ideally on your side of the bed.
You can also consider using a armbands or smartwatches. This certainly solves the problem for a little convenience trade-off.
If both of you are tracking, you can enable pair tracking, which filters out the partner’s activity.